Mathematics
/ 3. The theory of probabilities and
mathematical statistics
The
candidate of the physicist - mathematical sciences Kalzhanov M. U.
Kostanay
State University name A.Baitursynov
Measurement forms of distribution
laws in the formation of tracks
The peculiarity of the laws of distribution of random variables as the
measurement error of the instrument consists of their great variety. This is
due to the fact that the overall accuracy of the measuring instrument is
determined of a number of components.
In case if the components would be regarded as random
values then the summation of errors is reduced to the summation of the random
variables. In relation to adding up of casual sizes the laws of their
distribution change a form.
The law of sum distribution of
independent random variables ![]() with
distributions p1x è p2x, called composition,
expressed the convolution integral:
with
distributions p1x è p2x, called composition,
expressed the convolution integral:
![]()
The form's measurement of the laws of distribution at formation of
compositions occurs as follows:
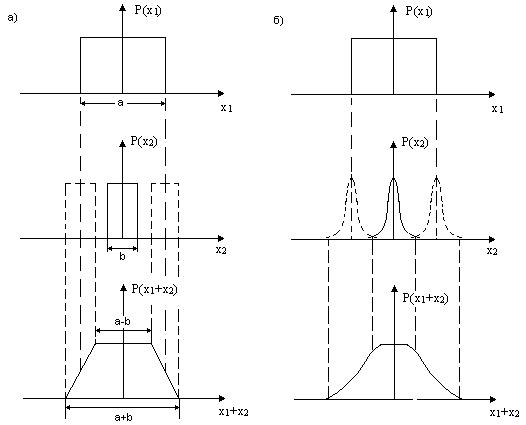
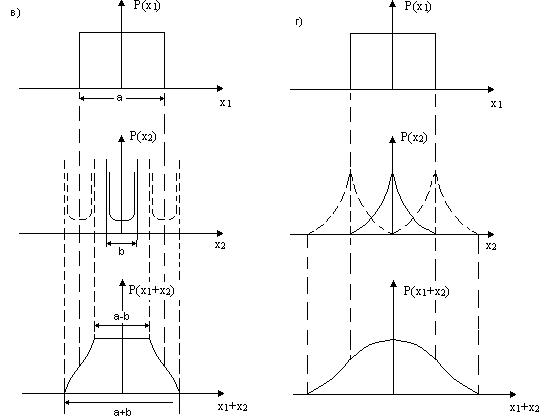
Fig. a) for the summation of the two errors are uniformly distributed
with a wide distribution, à > â the resulting error
distribution is in the form of a trapezoid with the upper base a-â and
a lower-to à+â.
This deformation can be represented as a blurring of sharply limited the
wider tails of the distribution (width à) by an amount less than the length of a wide distribution.
The composition of two identical (the width of à) uniform distribution
is triangular.
![]()
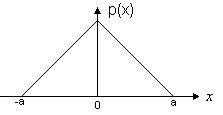
![]() in -a ≤ x ≤ 0
in -a ≤ x ≤ 0
![]() =
= ![]() in 0 ≤ x ≤ à
in 0 ≤ x ≤ à
in -a
> x; x >a
This so-called distribution of Simpson. This law of distribution is characteristic for random errors of digital
measuring instruments, in which the measured value is converted into a
proportional amount of time Tñ÷,
called the computation time. The measurement of this interval is performed by
counting pulses stable oscillator having a predetermined repetition period Òñ. The position
relative to the interval counting pulses Tñ÷
is random , the ratio between Tñ÷
and Tñ is also random, thus the maximum error of these values
are equal, i.e. à1=à2 => triangular distribution law .
Fig. á) Similarly, the composition is formed by uniform and normal
distributions , only the rise and fall of the edges of the resulting
distribution curve passes through the integral law of normal distribution.
Fig. â) with a uniform composition distribution and a width with the width
arksinusoidalnogo is curved trapezoid with the upper base à-â and a lower - to à+â and troughs for curves integral law arcsin-
distribution.
Fig. ã) Song uniform and Laplace distribution (two-sided exponential) has a
long, hollow decaying "tails" of the curve of the resulting
distribution.
The sheer scale of the curves in figure à-ã
is determined each time the fact that the area under
the curve of any of the density distribution should be equal to 1.
References:
1. A.D. Wentzel A course of lectures on casual processes . Ì., Science, 1982.
2. E.S. Wentzel, A.V. Ovcharov. Applied problems in the theory of
stochastic processes. Ì., Science, 1992.