Burakovski V.V.
Gomel State University, Belarus
Nonsymmetric
Dual-Ring Token-Passing Local Area Network
Abstract: A nonsymmetric dual-ring
token-passing local area network with N
stations in which each station has a single buffer is studied. The message
arrival streams at each station are assumed to be independent Poisson processes
with arrival rate λi for the i-th station, 1 ≤ i ≤ N.
The stationary probabilities of considered local area network and main
characteristics were obtained.
Introduction. Token-passing
is one of the most effective schemes to eliminate contention among stations in
a ring data-communication network. It involves passing the token, which is a
special bit pattern, from one station to another. The station that holds the
token has control over the medium for a predetermined amount of time, which is
referred as the token-holding time in the IEEE 802.5 standard [2].
Token-passing on a ring configuration ensures that all stations tied to the
ring have an opportunity to send messages. In a token ring network the token
circulates cyclicly among the stations so that arriving messages at stations
can be transmitted in a round fashion.
In this paper we propose a “dual-ring”
architecture with token passing protocol. The proposed approach is based on the
idea that there are two rings and two tokens circulate in network [1]. Ring 1
is referred as the forward channel. The token travelling along the forward
channel is referred as the forward token and is denoted as Tf.
The second ring is referred as the reverse channel. The token in this
ring is the reverse token and is denoted as Tr. The forward and the
reverse token move in opposite directions. In other words, the network stations
form a doubly linked list, which not only knows its “next” station but also is
aware of its previous station.We assume that Tf and Tr
arrive and leave the stations at the same moments.
Analytical model. A nonsymmetric
dual-ring token-passing local area network with N stations is considered. Each
station has a single buffer. The walk time for the forward or reverse token to
move from one station to the next one is assumed to be a constant equal to
δ. The service time for any station is a. During this time the station serves message if it is in buffer or
waits for the moment of departure if buffer is empty. The message arrival
streams at each station are assumed to be independent Poisson processes with
arrival rate λi for the i-th station,1 ≤ i ≤ N.
We consider the ordinary service discipline, which assumes that the
station transmits message when the token arrives, but none of those messages
that arrive after the token [4]. So no more than one message can be transmitted
from the station during Tf or Tr is at this station.
Let us denote by (i,j,k1,…kN) the state of the
dual-ring local area network, where i – is
the number of the station where Tf arrives and j – is the
number of the station where Tr arrives,
km – is the number of customers at the m-th station, 1 ≤ m
≤ N, at the moment when Tf and Tr arrive at
correspondent stations, km![]() {0,1}. The stationary probabilities of these states
are P (i,j,k1,…kN).
{0,1}. The stationary probabilities of these states
are P (i,j,k1,…kN).
1.
The
stationary probabilities. The behavior of our dual-ring network at the moments when Tf
and Tr arrive at the stations we can describe with the help of
periodical Markov chain. Let us denote by Aij, 1 ≤i, j ≤
N, the matrix of the transition probabilities, where i and j are the numbers of
the stations where Tf and Tr arrive correspondently. It
is evident that the numbers of the next stations where Tf and Tr
arrive from the stations i and j are i+1 and j-1. Let us denote by P(i,j) the
stationary probabilities vectors, 1 ≤i, j ≤ N.
The steady-state probabilities of considered queuing system are the
solution of the following matrix-vector system:
![]() ;
;
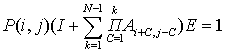 ;
;
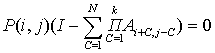 ,
,
where 1≤ i,j≤N, E is vector of 2N units, I –is
(2N ![]() 2N) matrix а units, Aij-
(2N
2N) matrix а units, Aij-
(2N![]() 2N) matrix of the transition
probabilities. These probabilities are
2N) matrix of the transition
probabilities. These probabilities are
![]()
where
0≤k,r≤2N-1, I{B}-is the indicator of set B, ![]() ,
,
αс –are the coefficients of the state (i, j, α1,…,
αN), βc –are the coefficients of the state
(i+1, j-1, β1,…, βN ).
2.
The main
characteristics. The main characteristics of the considered network are [3], [5], [6], [7]:
1) the probability that there are no messages in the network(the network
is empty);
2) the
probability that there are messages at each station;
3) the
load coefficient for the i-th station;
4) the
load coefficient of the network;
5) the
mean service time at each station;
6) the
mean return time for the Tf and Tr;
7) the
mean number of lost customers in the network;
8) the
mean number of busy stations;
9) the
mean delay time at the station.
The definition
of these characteristics is based on the steady – state probabilities (1). We
have obtained the dependence for the main characteristics of the network on
messages arrival rates.
3.
Conclusions. The present paper has
presented the mathematic model of nonsymmetric dual – ring token – passing
local area network with single buffer stations. The methodology used is based
on the cyclic Markovian processes [4]. It is interesting to investigate the LAN
with different service disciplines (k-limited, gated, Bernoulli) and finite
capacity buffers at each station. The processes in such networks are very
similar to the cell telephone stations widely used now. The description of the
symmetric dual – ring LAN is also very actual because of its complexity.
References
1. Wu Jean–Lien C., Wu
Jingshown, Huang Tien-Yu. A reliable token – passing bus LAN with reservation /
Wu Jean–Lien C., Wu Jingshown, Huang Tien-Yu // IEEE Infocom`89 Conf. Comput.
Commun. – 1989. – Vol 1. – Р. 1–8.
2. ANSI/IEEE 802.5
Standard – 1985. Token-passing ring access method and physical layer specification.
– IEEE Press, 1985. – 89 p.
3. Bux, W. Performance
issues in local – area networks / W. Bux // IBM Systems Journal. – 1984. –
Vol. 23, No 4. – Р. 351–374.
4. Takagi,
H. Analysis of polling systems / H. Takagi. – Cambridge, M.A. : MIT Press,
1989. – 198 p.
5. Бураковский, В.В. Маркерная кольцевая локальная сеть с
конечными буферами и ординарным обслуживанием сообщений / В.В. Бураковский
// Аэрокосмическое приборостроение России. Сер. 2, Авионика. – 1998. – Выпуск 1,
Санкт-Петербург, НААП, с. 63–67.
6. Бураковский, В.В., Медведев, Г.А. Кольцевая локальная
сеть с протоколом маркерного доступа / В.В. Бураковский, Г.А. Медведев
// Техника средств связи. Сер. Системы связи. – 1990. – Вып. 7. – С. 9–16.
7. Бураковский, В.В. Исследование кольцевых маркерных
локальных вычислительных сетей при помощи циклических марковских процессов /
В.В. Бураковский. – Гомель, 1997. – 15 с. (Препринт / Гомельский
государственный университет им. Ф. Скорины;
№ 31).